Adolescent Motivational Interviewing
Butler Center for Research

Using Motivational Interviewing to Treat Adolescents and Young Adults with Substance Use Disorders
A Case Study of Hazelden Betty Ford in Plymouth
Young people receiving treatment for substance use disorders (SUDs) present a unique clinical challenge. Though premature dropout from treatment happens with adults, as many as 50% of teens and young adults with substance use disorders do not complete treatment. In addition, many who do complete treatment do not fully engage with the treatment process (Gogel et al., 2011). Treatment engagement involves more than just being physically present; it involves actively taking part in all aspects of the treatment process and becoming emotionally invested in those processes as well as in peers attending the same services (Szapocznik et al., 2003; Wise et al., 2001). Another factor that may complicate treatment engagement is the fact that many adolescents enter treatment because of external pressures (such as parental insistence) and, as a result, may have low motivation to engage (Battjes et al., 2003). Because both retention and active engagement in treatment are associated with positive outcomes and recovery from substance use disorders (Williams and Chang, 2000; Moos & Moos, 2003; McWhirter, 2008), organizations offering treatment services to youth should focus on approaches that promote engagement and enhance the patient's intrinsic motivation and commitment to change.
The Hazelden Betty Ford Foundation has a facility in Plymouth, Minnesota, that focuses on providing substance abuse treatment to adolescents and young adults. In a recent interview with me, Dr. Joseph Lee, medical director of the Youth Continuum, stressed the importance of empathy in working with adolescent and young adult patients. A key piece of that work involves recognizing that empathy differs from identification. Empathy is the ability to imagine and accurately understand the feelings of another person and respond in a helpful way, and people with strong empathy can do this while maintaining a sense of being separate from that person (Buckman et al., 2011; Amsel, 2015). Identification, on the other hand, can be expressed as either relating to someone else so much that you lose a sense of yourself, or as identifying someone as so similar to yourself that you feel they must do and experience their situation as you do or did.
"We needed to take an honest look at how we were viewing and working with our patients," said Dr. Lee.

"This clinical introspection was especially critical as we began to treat more patients awash in the opioid epidemic. These kids are even more likely to drop out than other kids, and for them, the risk of going back out and using drugs can be fatal." The realization that empathic rapport is critical to helping the patient get better, combined with too many patients leaving treatment prematurely, particularly those with a high degree of clinical severity, prompted Lee and other clinical leaders to improve clinical practice at the therapist level.
"These kids are even more likely to drop out than other kids, and for them, the risk of going back out and using drugs can be fatal."
The Hazelden Betty Ford Foundation had therefore identified an opportunity to strengthen their empathy in working with patients, along with addressing the urgent needs to keep young patients in treatment, increase their engagement in the treatment process and increase their motivation to change. The next step in the process was to decide on a therapeutic approach to meet these objectives. As applied to patients with substance use disorders, motivational interviewing (MI) is a brief psychotherapy aimed at increasing the patient's motivation and ability to change his/her addictive behaviors (Miller, Zweben, DiClemente, & Rychtarik, 1992). It focuses heavily on therapists bringing empathy to the therapeutic process with clients. Figure 1 lists the five elements of the approach, as outlined by Miller et al. (1992). The first element is expressing empathy for the client, which can be done in a number of ways. Empathic communication signals dignity and respect for the client and helps prevent the development of a superior/inferior relationship where the therapist is telling the client what he or she should be feeling. Empathic communication involves reflective listening, communicating an acceptance of where the client is and supporting them in the process of change (Miller & Rollnick, 1991). In addition to its strong focus on empathy, MI was chosen by Plymouth staff because it is an evidence-based practice in treating substance use disorders, with several studies indicating its effectiveness for adolescent and young adult populations (Barnett et al., 2012; Brown et al., 2015).
"Once we identified that we needed to start doing MI in a more formalized, consistent way across our clinicians, we needed to map out and implement a plan for doing it," Dr. Lee observed.
As one might imagine, this plan was fairly complex. Though all staff in patient-facing roles received training, the implementation of Motivational Interviewing was heavily concentrated on two roles: alcohol/drug addiction counselors and addiction technicians. Addiction counselors are a core part of the residential program. They administer assessments, participate in treatment planning and engage in therapy with the patient around his or her unique needs and challenges. The addiction technicians help support the patient, including easing their transition between the medical services unit and the residential treatment unit, helping them get to appointments on time and filling in for other non-clinical aspects of treatment, such as conducting meditation exercises.
Systematic training of staff in these two roles was a vital first step in implementing Motivational Interviewing with patients. Several tactics were used as part of training, including the use of an Motivational Interviewing text, required attendance at several two-day workshops and in-person training by both external MINT-certified specialists and several Plymouth staff well-versed in Motivational Interviewing methods, including Dr. Lee; Travis Vanderbilt, an LADC counselor; and David Wells, a PhD-level psychologist in the mental health clinic. Once counselors and technicians were trained, Lee and other Plymouth Motivational Interviewing experts set up a process to measure how counselors conducted therapy sessions with patients. The process involves periodically taping therapy sessions and auditing them for elements of Motivational Interviewing. The conclusions of these audits are then shared with each counselor in regular supervision meetings with his/ her manager. "The results of the audits and feedback on the clinician's use of Motivational Interviewing are a vital part of the process and happens on an ongoing basis," says Dr. Lee. "But we focus on making these conversations collegial and constructive as opposed to punitive…the idea is to model Motivational Interviewing even in the practitioner/supervisor discussions."
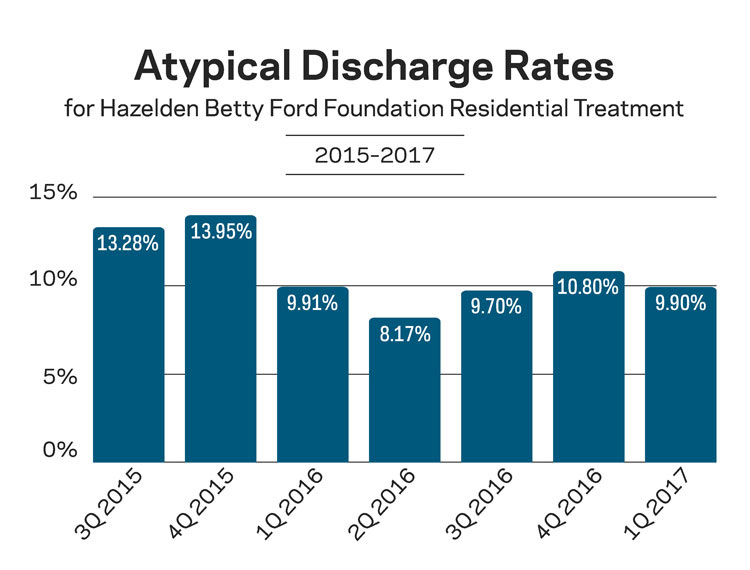
Successful implementation of Motivational Interviewing with Plymouth staff took several months, as is typically the case with clinical programs addressing behavioral health issues. By the middle of 2016, Motivational Interviewing was fully implemented and used consistently with all residential patients. Figure 2 shows atypical discharge rates for patients as a function of when they were discharged from the Plymouth residential program. These rates represent the percentage of patients who left treatment prematurely for various reasons (against staff advice, against medical advice, or occasionally at staff request). Over the last several quarters, the percentage of atypical discharges has been trending downward in a pattern consistent with the timeframe of motivational interviewing implementation. Only 9.9% of patients discharged in Q1 of 2017 left treatment prematurely, as opposed to 13.28% of patients in Q3 of 2015 (a 25% decrease). Though several other factors may have impacted these rates for example, an increase over time in the use of Suboxone for patients with opioid use issues the results are encouraging.
Qualitative feedback from staff members at Plymouth also suggests a positive impact of Motivational Interviewing on both staff and patients. Staff members described it as a "very person centered" approach, in part because it allows the clinician to effectively build rapport through empowerment rather than directives. Young patients are very receptive to the approach because they feel they are being worked with in a collaborative way, not talked down to or ordered to do certain things. Several staff members reported being able to help emotionally distressed patients change their mind about leaving treatment. In a couple of cases, the patient had left the facility, but the counselor was able to convince them to come back. Plymouth staff members directly attributed these outcomes to their use of Motivational Interviewing. "Motivational Interviewing is helping our patients because it reduces many of the impulsive decisions and encourages them to think through their actions before doing them," said one staff member. "It also helps them process through emotions they are not used to experiencing before making important decisions." Several counselors also reported that the therapeutic alliance formed with their patients has been strengthened through the use of Motivational Interviewing, which is quite important given the role of the alliance in predicting positive outcomes after treatment (Connors et al., 1997; Cook et al., 2015).
Behavioral health provider organizations wanting to implement evidence-based clinical practices in a highly accurate, reliable way can do so through an implementation science approach. At its core, implementation science involves the use of research and measurement to ensure that practices are implemented correctly within clinical settings (Proctor et al., 2009). The first step of the approach is to identify a practice that has a strong evidence base, meaning that it has been studied in a scientific manner and found to produce positive outcomes across studies. The second step involves mapping out how to deliver the clinical practice based on the organization's current structure, staffing models, clinical workflows and other processes related to care delivery. A key part of the second step is the training of staff directly administering the program or practice. Hazelden Betty Ford in Plymouth has completed these steps with regard to implementing motivational interviewing with residential patients. Clinical leaders and other staff will focus on subsequent steps over the coming months. This work will focus on evolving and standardizing the processes for measuring how effective each counselor is at implementing Motivational Interviewing with patients. Most importantly, counselors and supervisors will make sure that these assessments are used to continuously improve Motivational Interviewing practice.
"Motivational Interviewing is helping our patients because it reduces many of the impulsive decisions and encourages them to think through their actions before doing them."
This final step, though critical, is often overlooked by organizations implementing new clinical practices. It is one thing to implement something and occasionally measure how things are going. It is another thing to use what is learned and apply it back to care delivery on a continuous, long-term basis. As more behavioral health service providers use this model to bring evidence-based practices to patients, we can expect patient engagement and outcomes to improve.
Case Study October 2017. Download the Adolescent Motivational Interviewing case study.
Acknowledgements
Dr. Joseph Lee, medical director of the Youth Continuum
Joseph Lee, MD, has extensive experience in addiction treatment for youth and families from across the country and abroad, providing him an unparalleled perspective on emerging drug trends, co-occurring mental health conditions and the ever-changing culture of addiction. A triple board certified physician, Lee completed his medical degree at the University of Oklahoma, his adult psychiatry residency at Duke University Hospital and his fellowship in child and adolescent psychiatry at John Hopkins Hospital. He is a diplomat of the American Board of Addiction Medicine and is a member of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry's Substance Abuse Committee. He is also the author of Recovering My Kid: Parenting Young Adults in Treatment and Beyond, which provides a candid, helpful guide for parents in times of crisis.
References
- Amsel, B. (2015). Losing myself in your feelings: Empathy and identification. www.goodtherapy.org/blog/losing-my-self-inyour- feelings-empathy-and-identification-0925154 Barnett, E., Sussman, S., Smith, C., Rohrbach, L. A., & Spruijt-Metz, D. (2012). Motivational interviewing for adolescent substance use: A review of the literature. Addictive Behaviors, 37, 1325-1334.
- Battjes, R. J., Gordon, M.S., O'Grady, K. E., Kinlock, T. W., & Carsell, M. A. (2003). Factors that predict adolescent motivation for substance abuse treatment. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment, 24, 221-32.
- Brown, R. A., Abrantes, A. M., Minami, H., Prince, M. A., Bloom, E. L., Apodaca, T. R. et al. (2015). Motivational interviewing to reduce substance use in adolescents with psychiatric comorbidity. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment, 59, 20-29.
- Buckman, R., Tulsky, J. A., & Rodin, G. (2011). Empathic responses in clinical practice: Intuition or tuition? Canadian Medical Association Journal, 183, 569-571. doi:10.1503/ cmaj.090113
- Connors, G. J., Carroll, K. M., DiClemente, C. C., Longabaugh, R., & Donovan, D. M. (1997). The therapeutic alliance and its relationship to treatment participation and outcome. Journal of Consulting Clinical Psychology, 65, 588-598.
- Cook, S., Heather, N., & McCambridge, J. (2015). The role of the working alliance in treatment for alcohol problems. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 29, 371-381.
- Gogel, L. P., Cavaleri, M. A., Gardin, J. G. II & Wisdom, J. P. (2011). Retention and ongoing participation in residential substance abuse treatment: Perspectives from adolescents, parents and staff on the treatment process. Journal of Behavioral Health Services & Research, 38, 488-496.
- Horvath, A. O., & Bedi, R. P. (2002). The alliance. In J. C. Norcross (Ed.), Psychotherapy relationships that work: Therapist contributions and responsiveness to patients (37-69). New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
- McWhirter, P. T. (2008). Enhancing adolescent substance abuse treatment engagement. Journal of Psychoactive Drugs, 40, 173-182.
- Miller, W. R., and Rollnick, S. (1991). Motivational interviewing: Preparing people to change addictive behavior. New York: Guilford Press.
- Miller, W. R., Zweben, A., DiClemente, C. C., & Rychtarik, R. G. (1992). Motivational enhancement therapy manual: A clinical research guide for therapists treating individuals with alcohol abuse and dependence. National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism; Rockville, MD: NIAAA Project MATCH Monograph Series Volume 2, DHHS Publication No. (ADM) 92-1894.
- Moos, R. H., & Moos, B. S. (2003). Long-term influence of duration and intensity of treatment on previously untreated individuals with alcohol use disorders. Addiction, 98, 325-338.
- Proctor, E. K., Landsverk, J., Aarons, G., Chambers, D., Glisson, C., & Mittman, B. (2009). Implementation research in mental health services: An emerging science with conceptual, methodological, and training challenges. Administration and Policy in Mental Health, 36, 24-34. doi:10.1007/s10488-008-0197-4
- Szapocznik, J., Perez-Vidal, A., & Brickman, A. L., et al. (1988). Engaging adolescent drug abusers and their families in treatment: A strategic structural systems approach. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 56(4), 552-557.
- Williams, R. J. & Chang, S. Y. (2000). A comprehensive and comparative review of adolescent substance abuse treatment outcome. Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice, 7, 138-166.
- Wise, B. K., Cuffe, S. P., & Fischer, T. (2001). Dual diagnosis and successful participation of adolescents in substance abuse treatment. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment, 21, 161-165.
